Bone infections, medically known as osteomyelitis, are serious conditions that occur when bacteria or fungi invade the bone tissue. Although they are not very common, bone infections can lead to long-term complications if they are not diagnosed and treated on time. Therefore, understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for protecting long-term bone health.
What Are Bone Infections?
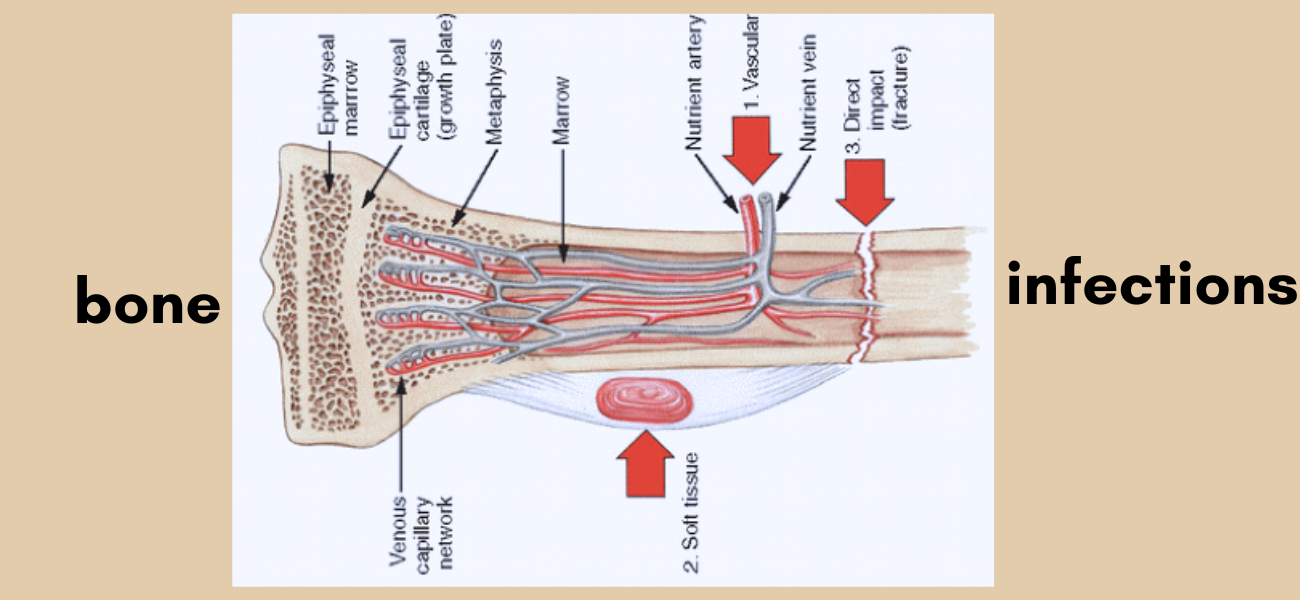
Bone infections develop when harmful microorganisms enter the bone through the bloodstream, nearby infected tissue, or direct exposure during injury or surgery. Over time, the infection can reduce blood flow to the bone, making healing more difficult. As a result, early detection plays a critical role in preventing permanent damage.
Moreover, bone infections can affect people of all ages, although children, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems are at higher risk.
Common Causes of Bone Infections
There are several reasons why bone infections may occur. Most often, bacteria are responsible, but fungal infections can also be a cause in rare cases.
Primary causes include:
- Open fractures or traumatic injuries
- Recent bone or joint surgery
- Spread of infection from nearby tissues
- Bloodstream infections
- Poor blood circulation
Additionally, conditions such as diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and immune disorders can increase susceptibility. Therefore, managing underlying health issues is equally important.
Symptoms of Bone Infections
The symptoms of bone infections may vary depending on the severity and duration of the infection. While some cases develop suddenly, others progress slowly and become chronic.
Common signs to watch for include:
- Persistent bone pain
- Swelling, warmth, or redness over the affected area
- Fever and chills
- Fatigue or weakness
- Difficulty moving the nearby joint
In chronic cases, symptoms may be milder but long-lasting. Consequently, ignoring persistent pain can delay diagnosis and worsen outcomes.
How Bone Infections Are Diagnosed
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Doctors usually begin with a physical examination and review of medical history. After that, diagnostic tests help confirm the presence of infection.
Diagnostic methods may include:
- Blood tests to detect infection markers
- X-rays to identify bone damage
- MRI or CT scans for detailed imaging
- Bone biopsy to identify the exact organism
Because early stages may not appear clearly on X-rays, advanced imaging is often recommended for precise assessment.
Treatment Options for Bone Infections
Treatment depends on the type, severity, and duration of the infection. In most cases, a combination of medical and, sometimes, surgical approaches is used.
Common treatment methods include:
- Long-term antibiotics or antifungal medications
- Intravenous (IV) antibiotics in severe cases
- Surgical removal of infected or dead bone tissue
- Stabilization of the affected bone
Furthermore, treating underlying conditions such as diabetes improves recovery and reduces the risk of recurrence.
Long-Term Effects of Untreated Bone Infections
If bone infections are left untreated, they can lead to serious complications. Over time, the infection may destroy bone tissue and spread to nearby joints.
Potential long-term effects include:
- Chronic bone pain
- Recurrent infections
- Bone deformity or weakness
- Reduced mobility
- Increased risk of fractures
In extreme cases, prolonged infection may even result in permanent disability. Therefore, early medical attention is crucial.
Prevention and Risk Reduction
Although not all bone infections can be prevented, certain steps can significantly reduce the risk.
Preventive measures include:
- Prompt treatment of wounds and fractures
- Maintaining good hygiene after surgery
- Managing chronic illnesses effectively
- Regular medical check-ups for high-risk individuals
Additionally, staying physically active and maintaining good nutrition helps support overall bone health.
When to See an Orthopedic Doctor
You should consult an orthopedic doctor if you experience persistent bone pain, swelling, or unexplained fever—especially after an injury or surgery. Early evaluation allows timely treatment and helps prevent long-term complications.
Conclusion
Bone infections are serious but treatable conditions when identified early. By understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms, and seeking appropriate treatment, patients can protect their bone health and prevent long-term damage. With proper medical care, most individuals recover well and regain normal function.


