Dr.Apoorv Dua
Move Freely, Live Fully. Expert Shoulder Care for a Pain-Free Life!
Shoulder pain shouldn’t limit your movement. Whether due to injury, arthritis, or stiffness, Dr. Apoorv Dua offers advanced treatments to restore strength, flexibility, and comfort.
- Shoulder Replacement
- Rotator Cuff Repair
- Arthroscopic Labral Repair
- Frozen Shoulder Arthroscopy
- Shoulder Fracture Fixation
Consult a Doctor
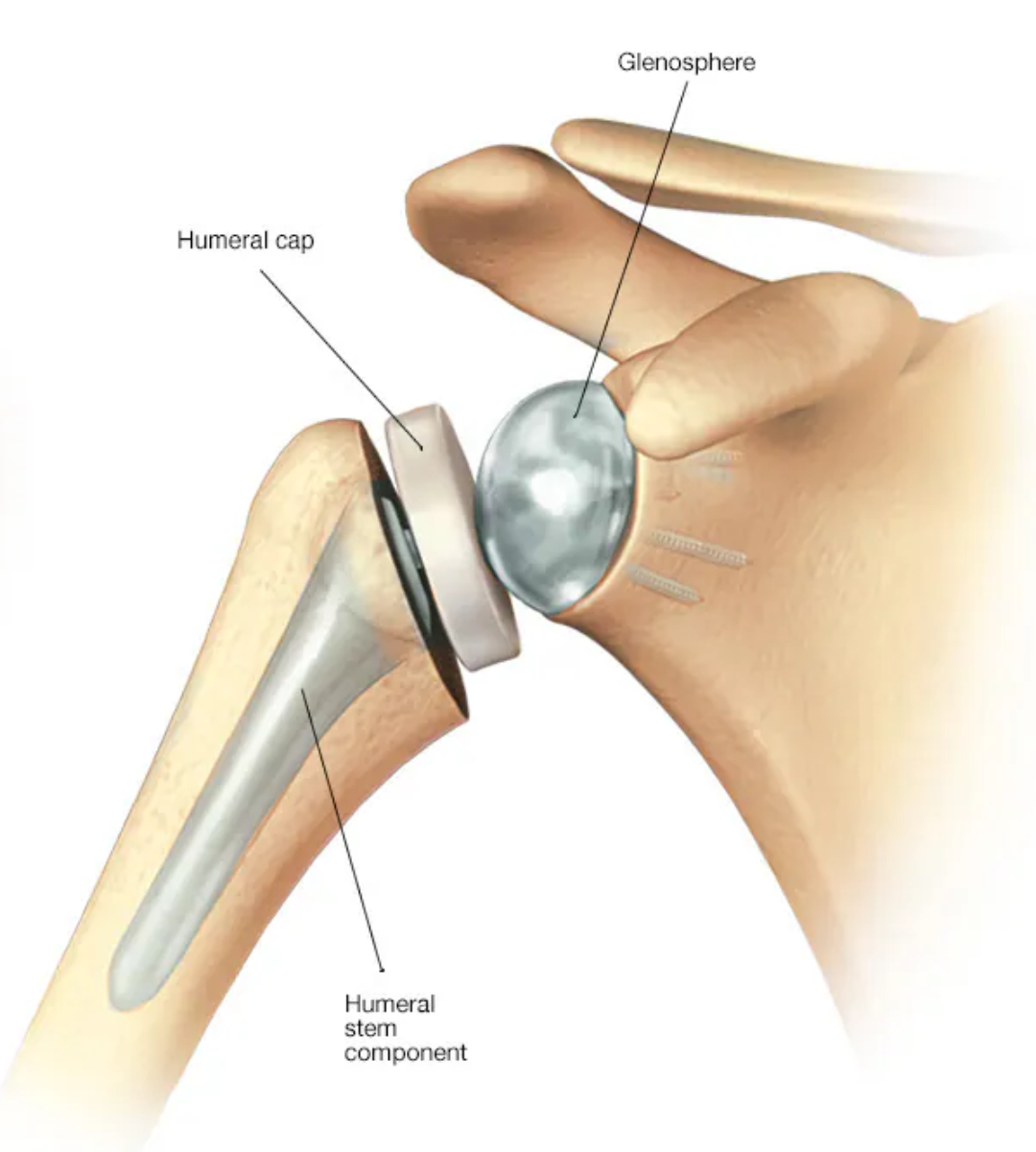
Shoulder Replacement
Shoulder replacement removes damaged areas of bone and replaces them with parts made of metal and plastic (implants). This surgery is called shoulder arthroplasty (ARTH-row-plas-tee).
The shoulder is a ball-and-socket joint. The round head (ball) of the upper arm bone fits into a shallow socket in the shoulder. Damage to the joint can cause pain, weakness and stiffness.
Shoulder implants are available in a few different shapes and a range of sizes. Replacement options include partial and total using either anatomic or reverse implants.
Shoulder replacement surgery has a high success rate, with patients often experiencing significant pain relief and improved mobility. Satisfaction rates for shoulder replacements are around 90%.
Know More
About Shoulder Replacement
-
 Symptoms
Symptoms
-
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
-
 How We Perform
How We Perform
-
 Why Is Treatment Needed?
Why Is Treatment Needed?
-
 Recovery
Recovery
-
 Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation
-
 Prevention
Prevention
Shoulder replacement surgery is done to relieve pain and other symptoms that result from damage to the shoulder joint.
Conditions that can damage the joint include:
- Osteoarthritis: Known as wear-and-tear arthritis, osteoarthritis damages the cartilage that covers the ends of bones and helps joints move smoothly.
- Rotator cuff injuries: The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder joint. Rotator cuff injuries sometimes can result in damage to cartilage and bone in the shoulder joint.
- Fractures: Fractures of the upper end of the humerus may require replacement, either as a result of the injury or when the prior surgery for fracture fixation has failed.
- Rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory disorders: Caused by an overactive immune system, the inflammation associated with rheumatoid arthritis can damage the cartilage and occasionally the underlying bone in the joint.
- Osteonecrosis: Some types of shoulder conditions can affect blood flow to the humerus. When a bone is starved of blood, it can collapse.
A doctor diagnoses conditions that may require shoulder replacement surgery by performing a physical exam, taking X-rays, and sometimes ordering other tests:
Physical exam
The doctor will check for any visible abnormalities or changes in the shoulder, and note pain levels during rest and activity.
X-rays
X-rays can confirm arthritis by showing loss of joint space in the shoulder joint.
CT scan
A CT scan may be needed to evaluate bone integrity.
MRI
An MRI can assess the condition of soft tissues, such as the rotator cuff tendon.
EMG test or nerve conduction study
If the doctor suspects nerve damage, they may order an EMG test or nerve conduction study.
Shoulder replacement surgery is a procedure that involves replacing the ball and socket of the shoulder joint with a prosthetic:
- Anesthesia
- Cut
- Remove the old parts
- Insert the new parts
- Close the incision
A shoulder replacement is a surgical procedure that replaces a damaged shoulder joint with an artificial component to treat pain and dysfunction. It’s often recommended when other treatments have failed and the patient is still experiencing severe pain and loss of function.
Some reasons why a shoulder replacement might be needed include:
- Arthritis
- Shoulder instability
- Severe pain
- Previous injuries
- Avascular necrosis
Shoulder replacement recovery varies from person to person, but it typically takes three to six months to fully recover.
Key Points:
- Pain and swelling: You can expect pain and swelling to taper off within the first four days.
- Physical therapy: You’ll start physical therapy within a week or two to help strengthen your shoulder muscles and improve movement.
- Activities: You should avoid activities that involve reaching or using your shoulder a lot, lifting heavy objects, or making sudden movements. You should also avoid putting your arm behind your back or using it to push yourself up
- Blood thinners: If you take a blood thinner, you should follow your doctor’s instructions carefully.
- Pain medication: Your doctor will tell you when and how to take pain medication.
Rehabilitation focuses on restoring shoulder function through physical therapy. This includes range of motion exercises, strength training, and pain management. The goal is to regain strength, flexibility, and stability in the shoulder. Functional activities are gradually reintroduced to help you return to daily tasks and activities with improved shoulder health.
Key Points:
- Tailored exercises to regain strength and mobility.
- Specific movements to improve shoulder flexibility.
- Exercises to rebuild shoulder strength and stability.
- Techniques and medications to manage post-rehabilitation discomfort.
- Gradual reintroduction to daily tasks and activities.
Preventing shoulder injuries involves regular exercise to strengthen the shoulder muscles, using proper techniques during physical activities, and avoiding overuse. Warm-up and stretching exercises help prepare the muscles for activity, while ergonomic adjustments ensure proper alignment and posture during daily tasks, reducing the risk of injury.
Key Points:
- Strengthening shoulder muscles to prevent injuries.
- Using correct techniques during physical activities and sports.
- Preventing repetitive strain on the shoulder joint.
- Preparing muscles before intense activities.
- Proper alignment and posture during daily tasks.
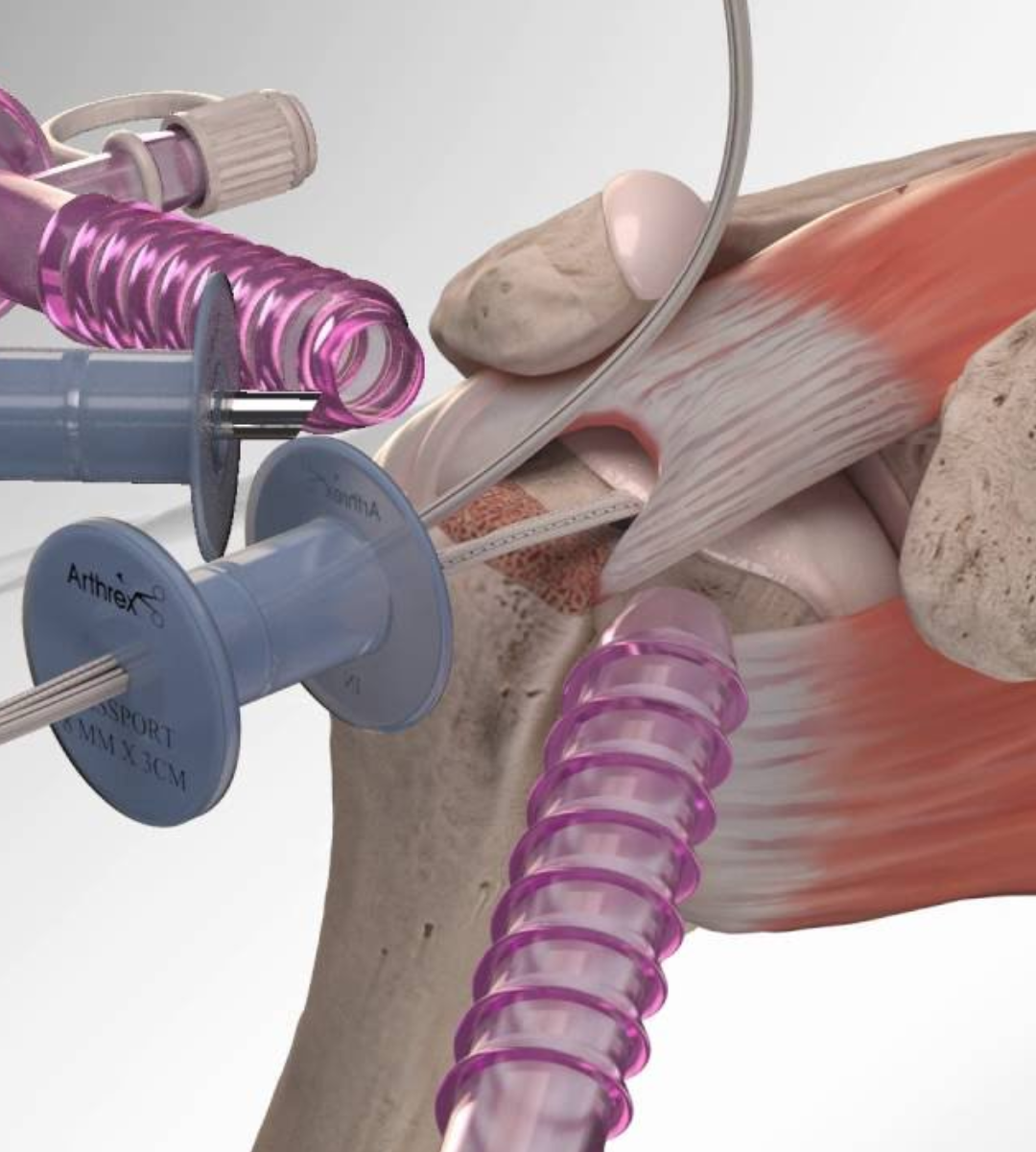
Rotator Cuff Repair
The rotator cuff is made up of muscles and tendons that hold the shoulder in place. It’s one of the most important parts of the shoulder. It allows you to lift your arm and reach up.
An injury to the rotator cuff, such as a tear, may happen suddenly when falling on an outstretched hand or develop over time due to repetitive activities. Rotator cuff degeneration and tears may also be caused by aging.
If your rotator cuff is injured, it may need surgery to repair it. This may include shaving off bone spurs that are pinching the shoulder or repairing torn tendons or muscles in the shoulder.
This usually involves reattaching the tendon to the head of the humerus. Surgical techniques that may be used to repair a tear of the rotator cuff include arthroscopy, open surgery,
or a combination of both. The goal of rotator cuff repair surgery is to help restore the function and flexibility of the shoulder and to relieve the pain that can’t be controlled by other treatments.
Know More
About Rotator Cuff Repair
-
 Symptoms
Symptoms
-
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
-
 How We Perform
How We Perform
-
 Why Is Treatment Needed?
Why Is Treatment Needed?
-
 Recovery
Recovery
-
 Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation
-
 Prevention
Prevention
Shoulder injuries are common. Athletes and construction workers often have rotator cuff injuries from repetitive movement and overuse of the shoulder. The rotator cuff may be damaged from a fall or other injury to the shoulder.
Symptoms of a rotator cuff injury include:
- Pain in the shoulder, especially when lifting, lowering, or rotating your arm
- Pain that worsens at night or when resting your arm
- A dull ache in the shoulder
- Weakness in the shoulder
- A popping, clicking, or crackling sensation when moving your arm
- Limited ability to move your arm
- Pain that prevents you from sleeping on your injured side
- Feeling like you’re being stabbed with a knife
During the physical exam, health care providers will press on different parts of the affected shoulder and move your arm into different positions. They’ll also test the strength of the muscles around your shoulder and in your arms.
Imaging tests may include:
- X-rays: Although a rotator cuff tear won’t show up on an X-ray, this test can visualize bone spurs or other potential causes for your pain — such as arthritis.
- Ultrasound: This type of test uses sound waves to produce images of structures within your body, particularly soft tissues such as muscles and tendons. It allows a provider to assess the structures of your shoulder during movement. It also allows a quick comparison between the affected shoulder and the healthy shoulder.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): This technology uses radio waves and a strong magnet. The images obtained display all structures of the shoulder in great detail.
Rotator cuff repair surgery is a procedure that involves reattaching the rotator cuff tendons to the upper arm bone, or humerus. The procedure can be performed using an arthroscope or with an open incision:
- Arthroscopic repair
A small camera called an arthroscope is inserted through a small incision in the shoulder joint. The surgeon uses the camera’s images to guide other instruments through additional small incisions to repair the torn tendon. This is the least invasive method and is usually performed as an outpatient procedure.
- Open repairA larger incision is made to repair the torn tendon. This approach may be used if the tear is too large or if arthroscopy is not an option.
Rotator cuff repair surgery is a treatment for rotator cuff injuries that aims to restore shoulder function, flexibility, and relieve pain. Surgery may be recommended if:
- You have persistent pain or weakness in your shoulder that doesn’t improve with other treatments
- You have a large tear (more than 3 cm)
- You have symptoms that have lasted 6 to 12 months
- You are very active and use your arms for overhead work or sports
- You have a recent, acute injury
- You have failed conservative treatment, such as physical therapy, for two months
Rotator cuff repair recovery time varies depending on the size of the tear and can take several months:
Rehabilitation focuses on restoring shoulder function through physical therapy. This includes range of motion exercises, strength training, and pain management. The goal is to regain strength, flexibility, and stability in the shoulder. Functional activities are gradually reintroduced to help you return to daily tasks and activities with improved shoulder health.
Key Points:
- Tailored exercises to regain strength and mobility.
- Specific movements to improve shoulder flexibility.
- Exercises to rebuild shoulder strength and stability.
- Techniques and medications to manage post-rehabilitation discomfort.
- Gradual reintroduction to daily tasks and activities.
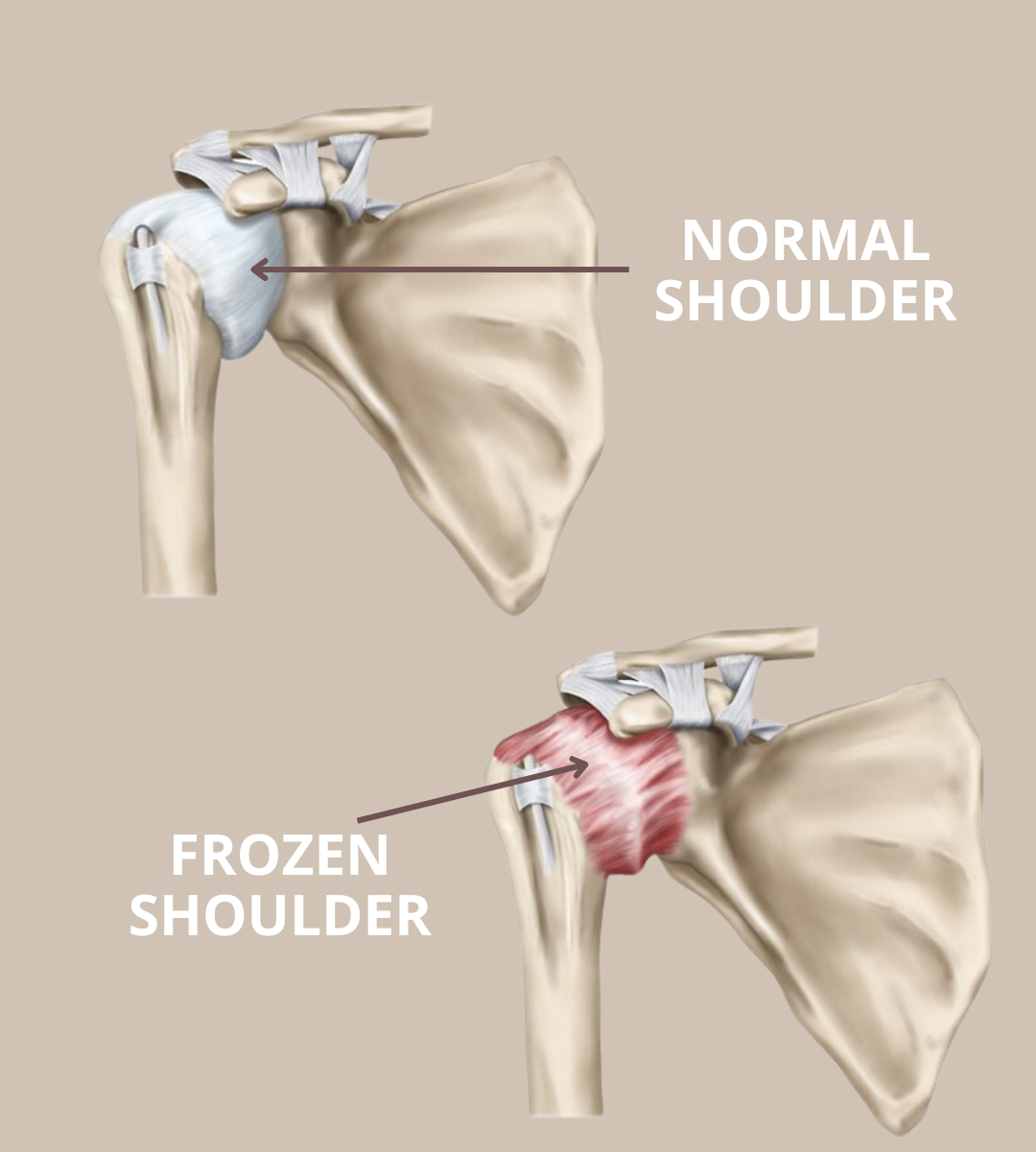
Frozen Shoulder
Frozen shoulder, also called adhesive capsulitis, causes pain and stiffness in the shoulder. Over time, the shoulder becomes very hard to move.
After a period of worsening symptoms, a frozen shoulder tends to get better, although full recovery may take up to 3 years. Physical therapy, with a focus on shoulder flexibility, is the primary treatment recommendation for frozen shoulder.
Frozen shoulder most commonly affects people between the ages of 40 and 60, and it occurs in women more often than men. In addition, people with diabetes and thyroid conditions are at an increased risk for developing frozen shoulder. However, a frozen shoulder can happen to anyone at any time. Sometimes it may happen after an injury or surgery.
Know More
About Arthroscopy for Frozen Shoulder
-
 Symptoms
Symptoms
-
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
-
 Why Is Treatment Needed?
Why Is Treatment Needed?
-
 Recovery
Recovery
-
 Prevention
Prevention
Frozen shoulder typically develops slowly in three stages.
- Freezing stage. Any movement of the shoulder causes pain, and the shoulder’s ability to move becomes limited. This stage lasts from 2 to 9 months.
- Frozen stage. Pain might lessen during this stage. However, the shoulder becomes stiffer. Using it becomes more difficult. This stage lasts from 4 to 12 months.
- Thawing stage. The shoulder’s ability to move begins to improve. This stage lasts from 5 to 24 months.
Physical exam: A doctor will examine the shoulder and arm, and test range of motion.
Medical history: A doctor will take a medical history and ask about symptoms.
Imaging tests: A doctor may order an MRI, CT scan, X-ray, or ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis. An MRI can show thickening of the joint capsule. An ultrasound can show thickening of the inferior capsule and coracohumeral ligament, rotator interval abnormality, and restricted range of motion.
Frozen shoulder, also known as adhesive capsulitis, is a condition that causes pain and stiffness in the shoulder. Treatment is needed to reduce pain and stiffness, and to maintain the shoulder’s range of motion. If left untreated, frozen shoulder can cause long-term pain and stiffness, and may lead to loss of mobility.
After surgery, physical therapy is necessary to maintain the motion that was achieved with surgery. Recovery may take 6 weeks to 3 months.
Long-term outcomes after surgery are generally good, with most patients having reduced or no pain and improved range of motion. In some cases, however, even after several years, the motion does not return completely and some degree of stiffness remains. Although uncommon, frozen shoulder can recur, especially if a contributing factor like diabetes is still present.
WHY US?
Why Choose Dr. Apoorv Dua
At our clinic, Dr. Apoov Dua provides expert care in Shoulder Replacement Surgery. With years of experience in orthopedic surgery, Dr. Dua specializes in minimally invasive techniques, ensuring faster recovery and improved long-term outcomes for his patients.
50,000+
Patients Experience

25,000+
Procedures

1000+
Trauma surgeries
5000
Joint Replacement Surgeries
Check Surgery Cost
We believe in transparency. You can enquire about the Surgery Cost and we will help you with complete detailed treatment process till your recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions About Shoulder Replacement
This surgery replaces the ball-and-socket joint of the shoulder with metal and plastic parts. It’s usually used as a last resort to treat severe damage, deformity, or chronic pain.
Shoulder replacement surgery is very successful at relieving pain, but it’s not perfect. You might still feel some pain when the weather changes or if you’re too active. The amount of improvement in range of motion is less predictable than pain relief.
Shoulder replacement recovery varies from person to person, but it typically takes three to six months to fully recover.
The rotator cuff is a group of four muscles that come together as tendons to form a “cuff,” or cover, over the head of the humerus (upper arm bone).
The four muscles — supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis and teres minor — originate from the scapula (shoulder blade). The rotator cuff tendons attach to the head of the humerus in bony spots referred to as the greater and lesser tuberosities.
Pain is the most common symptom, usually over the front and outer portion of the shoulder. Other symptoms include a dull pain, a tearing sensation, muscle weakness, and pain at night.
The type of repair performed is based on the findings at surgery.
- A partial tear may require only a trimming or smoothing procedure called a débridement.
- A full-thickness tear, which usually means the tendon is torn from its insertion on the humerus (the most common injury), is repaired directly to bone.
Three techniques are used for rotator cuff repair:
- Traditional open repair
- Mini-open repair
- Arthroscopic repair
Your orthopaedic surgeon can recommend which technique is best for you.
Frozen shoulder is a stiff and painful shoulder caused by inflammation, swelling and contraction of your shoulder lining (capsule). It is also known as adhesive capsulitis.
You should have less pain and be able to use your shoulder better.
If you smoke, stopping smoking now may reduce your risk of developing complications and will improve your long-term health.
Try to maintain a healthy weight. You have a higher risk of developing complications if you are overweight.
Regular exercise should help to prepare you for the operation, help you to recover and improve your long-term health. Before you start exercising, ask the healthcare team or your GP for advice.
Speak to the healthcare team about any vaccinations you might need to reduce your risk of serious illness while you recover. When you come into hospital, practise hand washing and wear a face covering when asked.
What Our Patients Say
Based on 160 reviews







I am Jaswanti pandey mother of two years old daughter manvi pandey.
I went to dr Apoorv Dua sir for my daughter hand fracture. He handled my daughter s case very nicely.He is a humble person and my daughter is recovering very nicely ....thank you sir.
"I have had a total knee replacement surgery performed by Dr. Apoorv Dua. From my first visit onwards ,I was able to place my trust in him. He took time to listen to all my concerns. His compassion and skills are remarkable. I received good preoperative and postoperative care. His expertise and exceptional care have made a great difference. I am happy about the results of my surgery and am grateful for the care given to me. I feel fortunate to have been treated by him. I would highly recommend him."
1. The x-ray technician seemed inexperienced and even after doing it 3 times the film was blurred
2. The dr saw the film and verbally told me there's no problem however when the report came 2 days later it said partial lumbar lordosis loss and some osteophytes.
3. The clinic held back our reports and refused to give it to us stating that the reporting person was on leave. This wasn't conveyed to us when we went for x-ray. Report was sent to us 2 days later after fighting and threatening to report them in consumer court.
It was just an extremely unethical behaviour. Will not recommend it at all.


